In an era where technological advancements intertwine seamlessly with our daily lives,the rise of Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)-connected wearables presents a dual-edged sword: innovation paired with an intricate web of privacy and security concerns. From health-tracking smartwatches to AI-enhanced fitness bands, these devices carry an immense potential to transform personal health management and open new doors to preventative care. however, as we increasingly entrust our most sensitive health data to these gadgets, pressing questions arise: Who truly owns this data? How is it protected? And what are the implications of its use by third parties? This article delves into the multifaceted landscape of IoMT-connected wearables, exploring the delicate balance between benefiting from cutting-edge technology and safeguarding individual privacy, security, and autonomy in an increasingly data-driven world.
Emerging Threats in IoMT-Connected Wearables Privacy Landscape
The proliferation of Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)-connected wearables has fundamentally transformed the healthcare landscape, but it has also introduced a complex web of privacy concerns. As wearable devices monitor everything from heart rates to sleep patterns,individuals are increasingly vulnerable to data breaches,unauthorized access,and misuse of sensitive health information. The seamless integration of these devices into everyday life not only enhances patient autonomy but also raises questions about who truly owns the data generated. With health data being a valuable asset, malicious actors may target it for exploitation, underscoring the necessity for robust security measures and regulations to protect users.
Moreover, the challenge lies in the fragmented regulatory landscape governing these devices. Variations in compliance requirements across jurisdictions can create loopholes, allowing some companies to sidestep stringent data protection protocols. The lack of standardization can lead to situations where consumers unknowingly consent to terms that undermine their privacy. In this surroundings,navigating the balance between innovation and safeguarding personal information is crucial. Stakeholders must collaborate to establish comprehensive policies that prioritize user privacy and foster trust, ensuring that the benefits of IoMT-connected wearables do not come at the expense of individual rights.
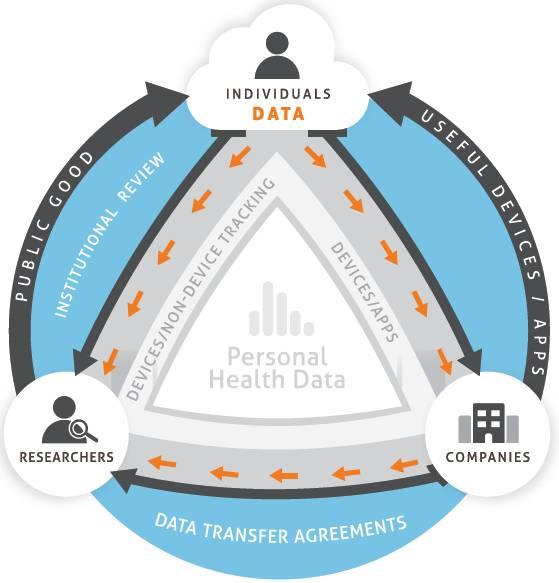
Decoding Security Challenges in Personal Health Data Transmission
The surge of Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) connected wearables presents an evolving landscape for personal health data transmission, characterized by both innovation and challenges. The transmission of sensitive health information, whether through smartwatches, fitness trackers, or other wearable devices, necessitates robust encryption protocols to safeguard users against unauthorized access.As these devices proliferate, understanding the potential vulnerabilities that could compromise data integrity becomes crucial. key concerns include:
- Data encryption: Ensuring that information transmitted is encoded against interception.
- Authentication measures: Implementing strong user verification processes to prevent unauthorized device access.
- Device integrity: Monitoring the security posture of connected devices regularly to identify any anomalous behavior.
Moreover, the legal landscape surrounding data ownership and privacy regulations complicates matters further. Although frameworks like HIPAA exist to protect patient information, the realities of global data transfer raise questions regarding jurisdiction and compliance. Wearables may collect a wealth of data,but clarity about ownership rights is frequently enough blurred,leaving users uncertain about who can access and utilize their information. Highlights include:
| Regulation | Focus Area | Implication for Users |
|---|---|---|
| HIPAA | healthcare Data Protection | Ensures confidentiality and limits data sharing. |
| GDPR | Personal Data Privacy | Empowers users with greater control over their data. |
| Data Ownership Laws | consumer Data Rights | Clarifies user rights regarding their personal data. |
Empowering Users through Clear Data ownership Frameworks
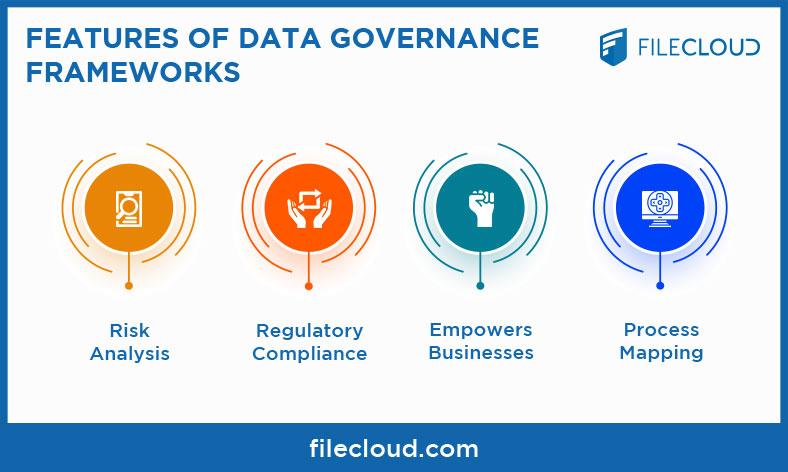
The integration of internet of Medical Things (IoMT) connected wearables into our daily lives has transformed healthcare, empowering users to take charge of their health.However, with this empowerment comes the critical challenge of establishing clear frameworks for data ownership. Users must have a defined understanding of their rights regarding the data collected by these devices. Key principles of data ownership include:
- Clarity: Users should be fully informed about what data is collected,how it is used,and who has access to it.
- Control: Individuals must have the ability to manage their data, including options for editing, downloading, and deleting their information.
- Consent: Clear definitions of consent must be in place,allowing users to opt-in or out of data sharing seamlessly.
Moreover, to further reinforce a user-centric approach, companies manufacturing IoMT devices must establish robust data ownership policies that prioritize user interests. By implementing effective frameworks, stakeholders can encourage trust and foster a positive relationship with users. A comparison of potential frameworks can illustrate the varying degrees of user empowerment:
| Framework | User Empowerment Level | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | Low | No user control, limited transparency |
| Intermediate | Moderate | Some control options, medium transparency |
| Advanced | High | Full control, complete transparency, user-driven consent |

Building Trust: Best Practices for Manufacturers and Consumers
Establishing trust between manufacturers of IoMT-connected wearables and consumers hinges on transparency and dialog. Companies must convey clear information regarding how data is collected, used, and shared. This commitment to transparency includes the implementation of user-pleasant privacy policies and terms of service that demystify data handling practices. By adopting open communication channels,manufacturers can actively engage with consumers,addressing concerns and answering questions about data privacy and security.
Moreover, empowering consumers with comprehensive controls over their own data is crucial in building mutual trust. Providing options for users to manage their privacy settings can foster a sense of ownership, enhancing their overall confidence in the device. Consider the following practices that can strengthen the relationship between manufacturers and consumers:
- Regular updates: Keep software and firmware up-to-date to protect against vulnerabilities.
- Easy opt-in/out options: Ensure that users can easily customize their data-sharing preferences.
- Education: Offer resources to help consumers understand their rights regarding data ownership.
In Conclusion
As we navigate the intricate landscape of IoMT-connected wearables, it becomes evident that the balance between innovation and responsibility hangs delicately in the air. These devices hold the potential to revolutionize healthcare, enhancing our understanding of personal health while empowering us with data-driven insights.Yet, with this advancement comes an equal measure of concern regarding privacy, security, and data ownership.
Our exploration into these critical themes has highlighted the urgent need for robust frameworks that not only protect user data but also foster transparency and trust. As consumers, we must remain vigilant in advocating for our rights, ensuring that the data gathered from our wearables is treated with the respect it deserves.
In closing, the future of IoMT-connected wearables is rife with promise, but it is imperative that we approach this future with a discerning eye and a proactive mindset. By embracing both the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead, we can pave the way for a digital health ecosystem that prioritizes user autonomy and safeguards our most personal information. The conversation has just begun—let us continue to engage, question, and shape the narrative around the intersection of technology and personal privacy.





